
In this example, which uses a MAC address reserved for documentation, the search returns the OUI itself and the database information for that OUI:
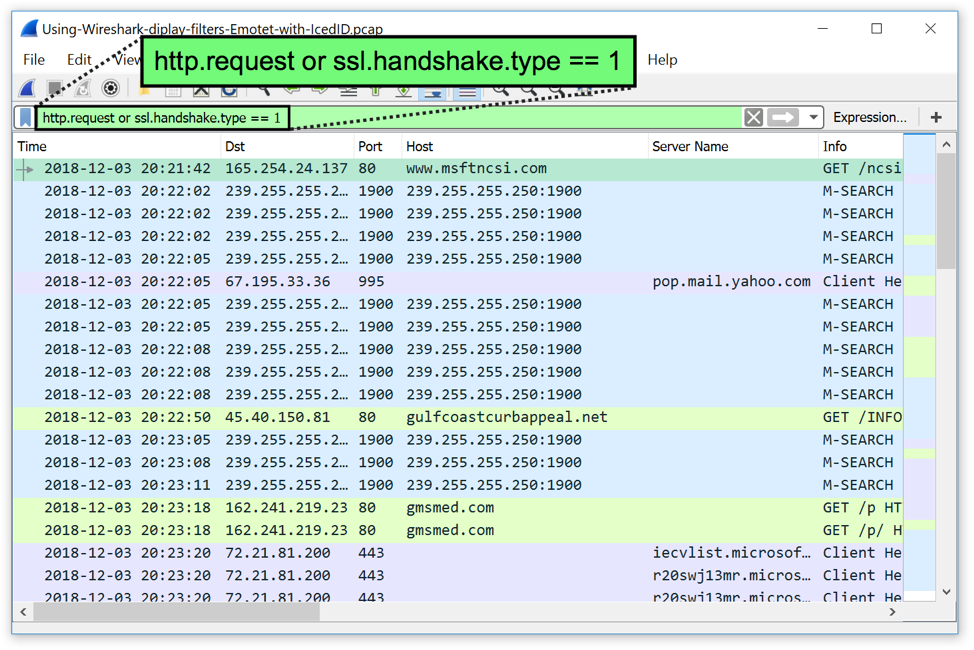
The search queries the Wireshark manufacturer database and returns the OUI vendor name and any other descriptive information stored for that OUI. An OUI search typically looks at a hexadecimal MAC address like this: OUIs are tracked through the IEEE Registration Authority, and Wireshark maintains an API called manuf that provides a mechanism for searching against the Wireshark manufacturer database, an open source collection of all known OUI prefixes - the first three octets of the MAC address.
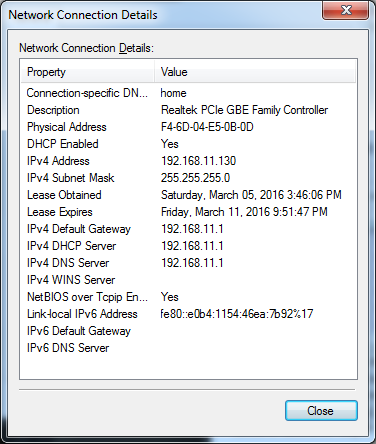
Modern network interfaces like those used for Ethernet or Wi-Fi are uniquely identified in six octets (48 bits) of a MAC address. These addresses uniquely identify the network interfaces on physical networks and consist of two parts: The first three octets (bytes) of the addresses are associated with the manufacturer or vendor of the device's NIC, and the second three octets uniquely identify the NIC itself. Most networked devices use Ethernet or Wi-Fi NICs and have 48-bit MAC addresses. This tutorial shows how to use Wireshark's OUI lookup tool from within the Wireshark application, as well as how to do OUI lookup from any internet-connected device.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
